Assay Sample Testing: A Comprehensive Guide for Clinical Research Organizations (CROs)
Assay sample testing is a critical component of clinical research, particularly for Clinical Research Organizations (CROs). As a CRO, understanding the intricacies of assay sample testing can significantly impact the quality and efficiency of your research processes. This article delves into the various aspects of assay sample testing, providing you with a detailed and multi-dimensional overview.
Understanding Assay Sample Testing
Assay sample testing involves the analysis of biological samples to measure the concentration of a specific substance, such as a drug or a biomarker. This process is essential for clinical research, as it helps researchers determine the efficacy and safety of a drug or treatment.
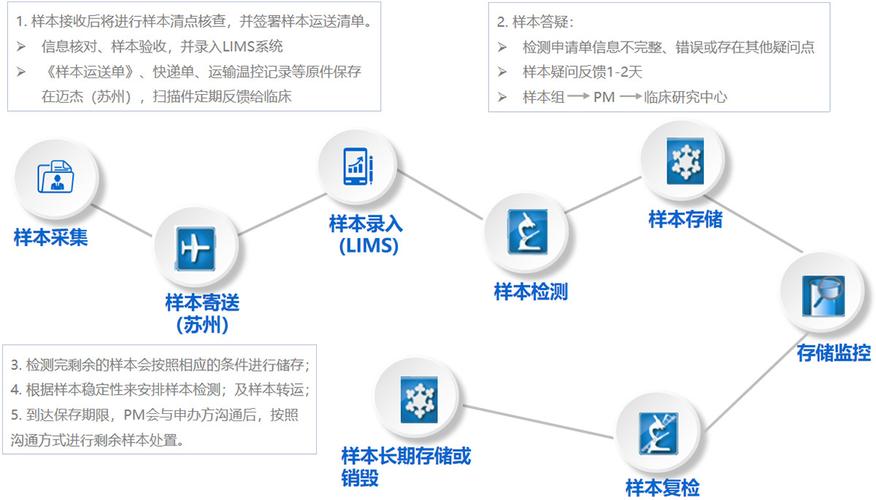
Assay sample testing can be categorized into several types, including:
-
Quantitative assays: These assays measure the amount of a substance in a sample.
-
Qualitative assays: These assays determine the presence or absence of a substance in a sample.
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs): These assays use antibodies to detect and measure the concentration of a substance in a sample.

-
Flow cytometry: This technique measures the physical and chemical properties of cells and particles in a fluid.
The Importance of Assay Sample Testing in Clinical Research
Assay sample testing plays a crucial role in clinical research for several reasons:
-
Drug development: Assay sample testing helps researchers determine the concentration of a drug in the body, which is essential for optimizing dosing regimens.
-
Biomarker discovery: By measuring the levels of specific biomarkers, researchers can identify potential targets for new therapies.
-
Monitoring treatment efficacy: Assay sample testing allows researchers to monitor the effectiveness of a treatment over time.
-
Assessing safety: By analyzing the levels of toxic substances in a sample, researchers can assess the safety of a drug or treatment.
The Process of Assay Sample Testing
The process of assay sample testing typically involves the following steps:
-
Sample collection: Biological samples, such as blood, urine, or tissue, are collected from patients.
-
Sample preparation: The samples are processed to remove impurities and concentrate the target substance.
-
Assay procedure: The prepared samples are analyzed using the appropriate assay technique.
-
Data analysis: The results of the assay are analyzed to determine the concentration of the target substance.
-
Reporting: The results are reported to the researchers, who can use the information to make informed decisions.
The Role of CROs in Assay Sample Testing
CROs play a vital role in assay sample testing, as they provide the necessary expertise and resources to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. Here are some key responsibilities of CROs in assay sample testing:
-
Sample collection and handling: CROs ensure that samples are collected and handled according to established protocols to maintain sample integrity.
-
Assay development and validation: CROs develop and validate assays to ensure they are accurate, precise, and reproducible.
-
Quality control: CROs implement quality control measures to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the assay results.
-
Data analysis and reporting: CROs analyze the data and generate comprehensive reports for the researchers.
Challenges and Solutions in Assay Sample Testing
Assay sample testing can be challenging due to various factors, such as sample variability, assay limitations, and data interpretation. Here are some common challenges and their corresponding solutions:
