Understanding ADCC: A Comprehensive Guide
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) is a crucial mechanism in the immune response against pathogens and cancer cells. This article delves into the intricacies of ADCC, exploring its definition, mechanism, clinical significance, and the role of ADCC receptors (FcRs) in this process.
What is ADCC?
ADCC is a process where effector cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, recognize and kill target cells that are coated with antibodies. This mechanism plays a vital role in eliminating virus-infected cells, tumor cells, and other pathogens from the body.
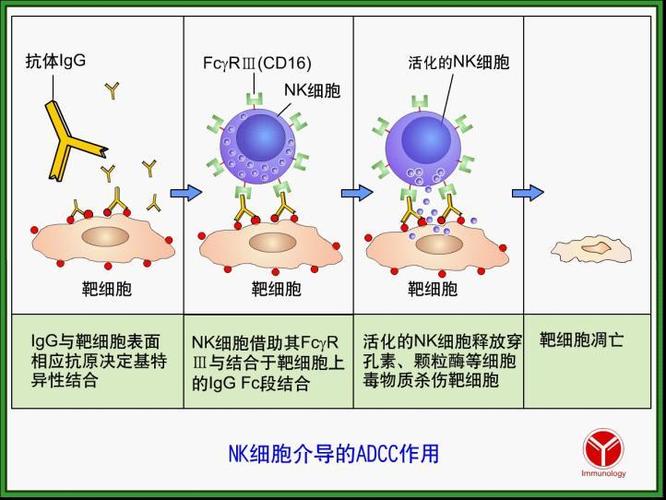
How Does ADCC Work?
ADCC involves the binding of antibodies to specific antigens on the surface of target cells. The antibodies used in ADCC are typically immunoglobulin G (IgG) molecules, which have two Fab (antigen-binding) domains and one Fc (fragment crystallizable) domain. The Fab domains bind to the antigens on the target cell surface, while the Fc domain interacts with FcRs on the surface of effector cells.
There are several types of FcRs, including FcRIIIa, FcRIIa, and FcRI. FcRIIIa is the most important FcR for ADCC, as it is expressed on NK cells and some macrophages. When the Fc domain of the antibody binds to FcRIIIa, it triggers the effector cell to release cytotoxic substances, leading to the death of the target cell.
The Role of ADCC in Clinical Settings
ADCC has significant clinical implications, particularly in the treatment of cancer. Monoclonal antibodies that target cancer-specific antigens can induce ADCC, leading to the destruction of tumor cells. This mechanism is the basis for several approved cancer immunotherapies, such as trastuzumab (Herceptin) for breast cancer and rituximab (Rituxan) for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
ADCC is also being investigated as a potential therapeutic strategy for other diseases, such as HIV infection and hepatitis C. By enhancing the ADCC activity of antibodies, it may be possible to develop more effective treatments for these conditions.
The Importance of ADCC Receptors
The expression of FcRs on effector cells is crucial for the effectiveness of ADCC. Certain genetic variations in FcRs can affect the ADCC response, leading to differences in the clinical outcomes of antibody-based therapies. For example, individuals with certain FcRIIIa polymorphisms may have reduced ADCC activity, which could impact the efficacy of cancer immunotherapies.
Enhancing ADCC Activity
Several strategies are being explored to enhance the ADCC activity of antibodies. These include:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Fc engineering | Modifying the Fc domain of the antibody to improve its binding to FcRs |
| Fc glycosylation | Adding sugar molecules to the Fc domain to enhance its interaction with FcRs |
| Fc multimerization | Increasing the number of Fc domains on the antibody to increase its binding to FcRs |
By improving the ADCC activity of antibodies, it may be possible to develop more effective and targeted therapies for a wide range of diseases.
Conclusion
ADCC is a critical mechanism in the immune response against pathogens and cancer cells. Understanding the intricacies of ADCC and the role of FcRs can help in the development of more effective therapies for various diseases. As research in this area continues to advance, we can expect to see new and improved treatments that harness the power of ADCC.
