Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease: A Comprehensive Overview for You
Alzheimer’s disease, often referred to as AD, is a complex neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by progressive memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes. In this article, we delve into the various aspects of Alzheimer’s disease, providing you with a detailed and comprehensive understanding of this condition.
What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is a form of dementia, which is a general term for memory loss and other cognitive impairments that affect daily functioning. It is the most common cause of dementia, accounting for about 60-80% of cases. The disease primarily affects older adults, though it can occur in younger individuals.
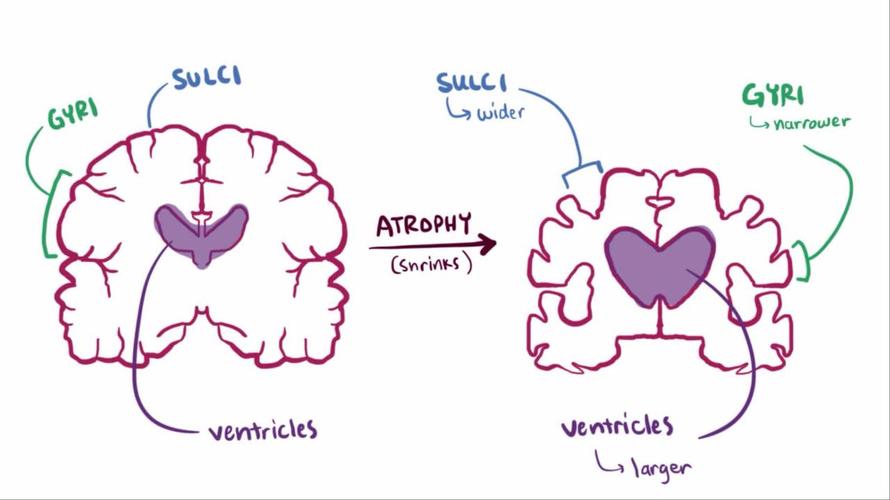
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some of the key risk factors include:
-
Age: The risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease increases with age.
-
Family History: Having a family member with Alzheimer’s disease increases your risk.
-
Genetic Factors: Certain genes may predispose individuals to the disease.

-
Head Trauma: A history of head trauma, such as a concussion, may increase the risk.
-
Cardiovascular Health: Poor cardiovascular health, including high blood pressure and high cholesterol, may contribute to the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Alzheimer’s disease typically progresses through several stages, with symptoms becoming more pronounced over time. The early stages may include:
-
Mild Memory Loss: Difficulty remembering recent events or names.
-
Changes in Behavior: Increased irritability, mood swings, or social withdrawal.
-
Language Difficulties: Difficulty finding the right words or understanding spoken or written language.
As the disease progresses, symptoms may worsen and include:
-
Severe Memory Loss: Difficulty recalling even personal information.
-
Impaired Judgment: Difficulty making decisions or recognizing danger.
-
Behavioral Changes: Agitation, aggression, or delusions.
-
Loss of Motor Skills: Difficulty walking, speaking, or performing daily tasks.
Diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease can be challenging, as there is no single test to confirm the diagnosis. Doctors typically use a combination of medical history, cognitive tests, and brain imaging to make a diagnosis.
Treatment and Management
There is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but there are treatments and strategies that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
-
Medications: Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine are commonly prescribed to help manage cognitive symptoms.
-
Non-Medical Interventions: Physical exercise, cognitive training, and social activities can help maintain cognitive function and improve mood.
-
Supportive Care: Managing behavioral symptoms and providing emotional support to both the patient and caregivers.
Prevention and Support
While there is no definitive way to prevent Alzheimer’s disease, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk, such as:
-
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help reduce your risk.
Support for individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and their caregivers is crucial. Support groups, counseling, and respite care can provide emotional and practical assistance.
Conclusion
Alzheimer’s disease is a challenging condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you or your loved ones cope with the disease. By taking proactive steps to reduce risk factors and seeking support, you can improve
