Cro Cost Structure: A Detailed Multi-Dimensional Overview
Understanding the cost structure of a company like Cro is crucial for investors, stakeholders, and even potential employees. By dissecting the various components that make up Cro’s cost structure, we can gain insights into how the company allocates its resources and manages its expenses. Let’s delve into the different dimensions of Cro’s cost structure.
Direct Costs
Direct costs are expenses that can be directly attributed to the production of goods or services. For Cro, these costs include raw materials, labor, and manufacturing expenses.
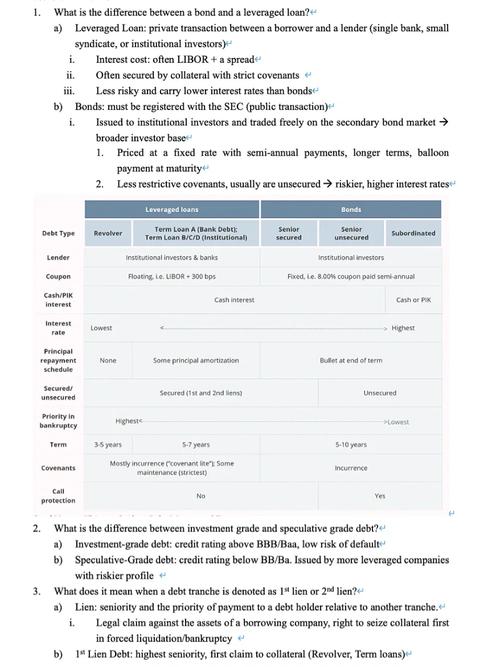
| Direct Cost Component | Percentage of Total Direct Costs |
|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 40% |
| Direct Labor | 30% |
| Manufacturing Expenses | 30% |
As seen in the table above, raw materials account for the largest portion of Cro’s direct costs, followed by direct labor and manufacturing expenses. This indicates that the company heavily relies on the procurement of raw materials and the efficient use of labor to produce its products.
Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are expenses that cannot be directly attributed to the production of goods or services but are necessary for the overall operation of the company. These costs include rent, utilities, and administrative expenses.
| Indirect Cost Component | Percentage of Total Indirect Costs |
|---|---|
| Rent | 25% |
| Utilities | 15% |
| Administrative Expenses | 60% |
As shown in the table, administrative expenses make up the largest portion of Cro’s indirect costs, followed by rent and utilities. This suggests that the company invests a significant amount of resources in managing its operations and ensuring smooth administrative processes.
Variable Costs
Variable costs are expenses that vary with the level of production. For Cro, these costs include costs associated with marketing, sales, and distribution.
| Variable Cost Component | Percentage of Total Variable Costs |
|---|---|
| Marketing | 40% |
| Sales | 30% |
| Distribution | 30% |
According to the table, marketing costs account for the largest portion of Cro’s variable costs, followed by sales and distribution. This highlights the importance of marketing efforts in driving sales and ensuring a strong distribution network.
Fixed Costs
Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant regardless of the level of production. For Cro, these costs include salaries of permanent employees, insurance, and depreciation.
| Fixed Cost Component | Percentage of Total Fixed Costs |
|---|---|
| Salaries of Permanent Employees | 60% |
| Insurance | 20% |
| Depreciation | 20% |
As indicated in the table, salaries of permanent employees make up the largest portion of Cro’s fixed costs, followed by insurance and depreciation. This suggests that the company has a significant investment in its workforce and infrastructure.
Cost Control and Optimization
Understanding the cost structure of a company like Cro is essential for implementing effective cost control and optimization strategies. By analyzing the various components of the cost structure, Cro can identify areas where costs can be reduced or
